
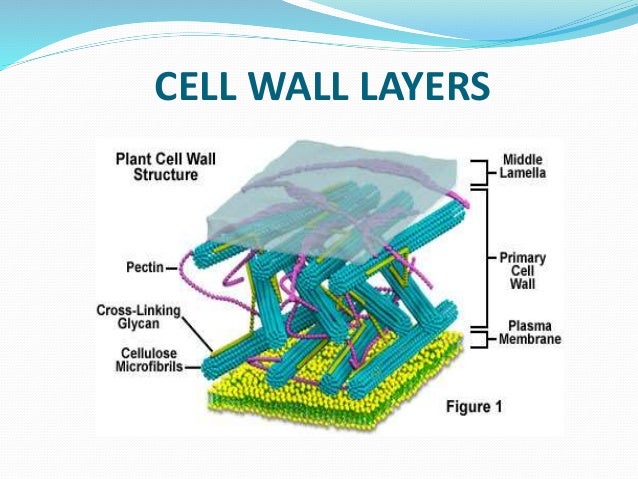

Generally, the cell wall is the outer covering of a cell, present adjacent to the cell membrane, which is also called the plasma membrane. The cell wall’s cellular component is present exclusively in eukaryotic plants, fungi, and a few prokaryotic organisms The cell wall also provides shape, support, and protection to the cell and its organelles. Cell wall composition varies according to the organism and is permeable and also it separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior environment. A cell wall is also defined as the non-living component, covering the outermost layer of a cell. Though it is an inactive product serving mainly mechanical and structural purposes. The cell wall is mainly responsible for many of the characteristics that distinguish plant cells from animal cells.

The structure of the cell wall permits many minor molecules to go through it, but not bigger molecules that could harm the cell.Ī cell wall is a specialized form of the extracellular matrix that surrounds every cell of a plant. The cell wall can also deliver protection from pathogens such as bacteria that try to raid the cell. It is elastic but delivers strength to the cell, which adds protection to the cell against bodily damage. The cell wall has some different functions. The cell wall has changed many different times among different sets of organisms. The resources that make up the cell wall vary depending on the type of organism. The cell wall provides strength and structural support to the cell and can regulate to some amount, what kind and concentration of molecules or particles enter and leave the cell. All cells contain cell membranes, but normally only plants, fungi, most bacteria, algae, and archaea have cells with cell walls. A cell wall is an external layer covering certain cells that is external to the cell membrane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
